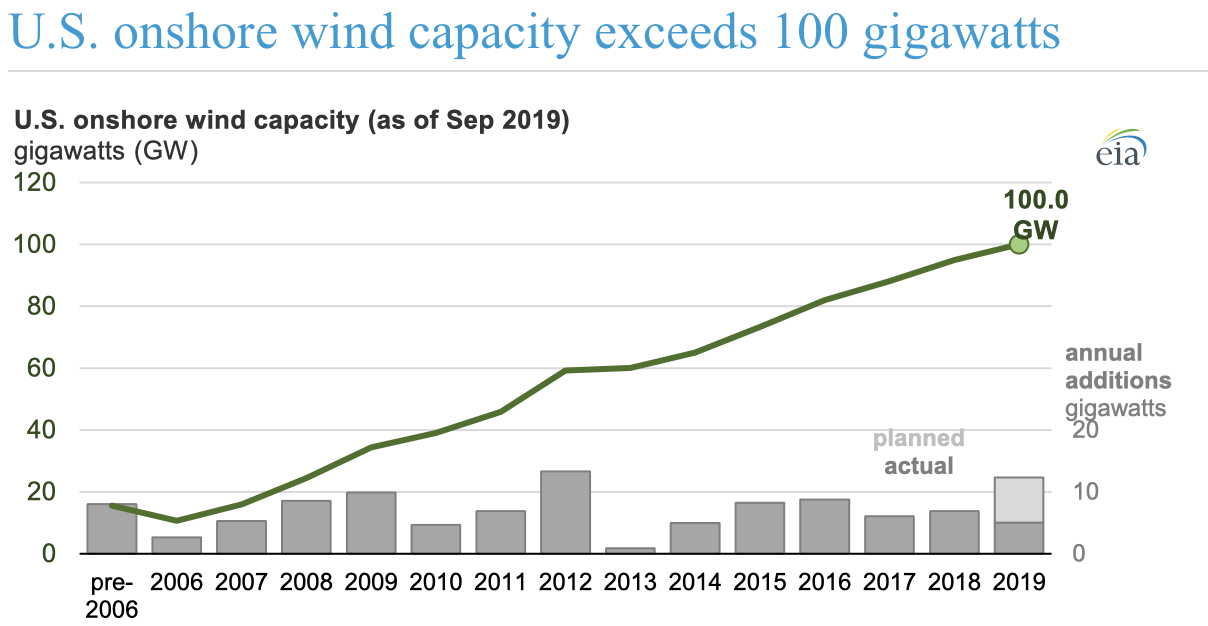
Cumulative U.S. installed onshore wind capacity exceeded 100 gigawatts (GW) on a nameplate capacity basis as of the end of September 2019, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration’s (EIA) Preliminary Monthly Electric Generator Inventory. More than half of that amount has been installed since the beginning of 2012. The oldest wind turbines still operating in the United States came online as early as 1975.
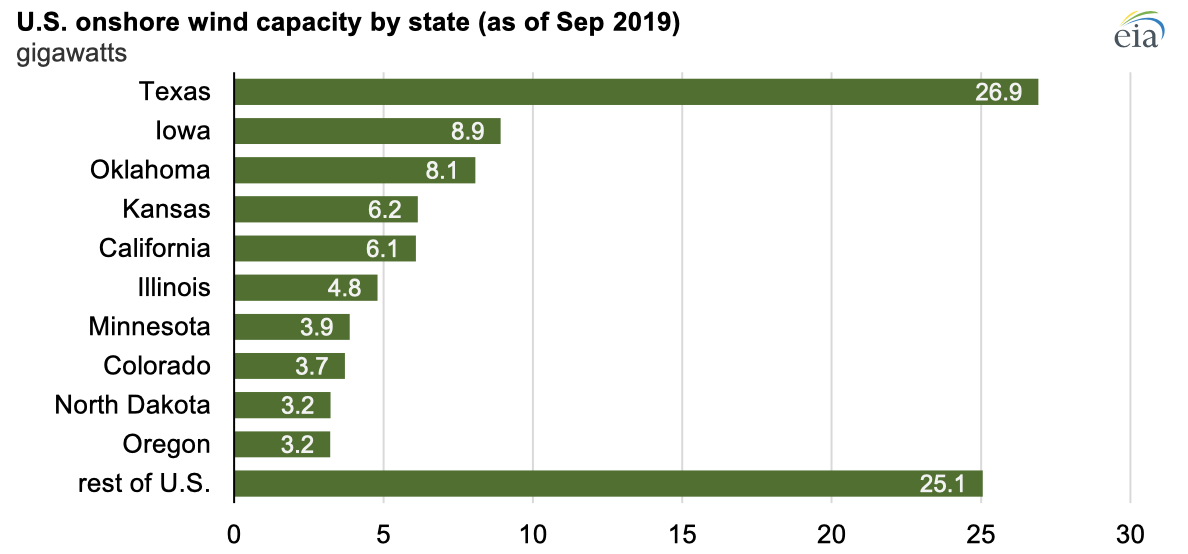
As of the third quarter of 2019, 41 states had at least one installed wind turbine. Texas had the most capacity installed, at 26.9 GW, followed by Iowa, Oklahoma, and Kansas. These four states accounted for half of the total U.S. installed wind capacity.
In the United States, wind turbines tend to come online late in the year. Based on information reported in the Preliminary Monthly Electric Generator Inventory, EIA expects that an additional 7.2 GW of capacity will come online in December 2019. EIA also expects that another 14.3 GW of wind capacity will come online in 2020. If realized, the United States would have about 122 GW of wind capacity by the end of next year.
Principal contributor: Richard Bowers





